ملف:Supercomputing-rmax-graph.png
حجم هذه المعاينة: 796 × 600 بكسل. الأبعاد الأخرى: 319 × 240 بكسل | 637 × 480 بكسل | 812 × 612 بكسل.
الملف الأصلي (812 × 612 بكسل حجم الملف: 22 كيلوبايت، نوع MIME: image/png)
تاريخ الملف
اضغط على زمن/تاريخ لرؤية الملف كما بدا في هذا الزمن.
| زمن/تاريخ | صورة مصغرة | الأبعاد | مستخدم | تعليق | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
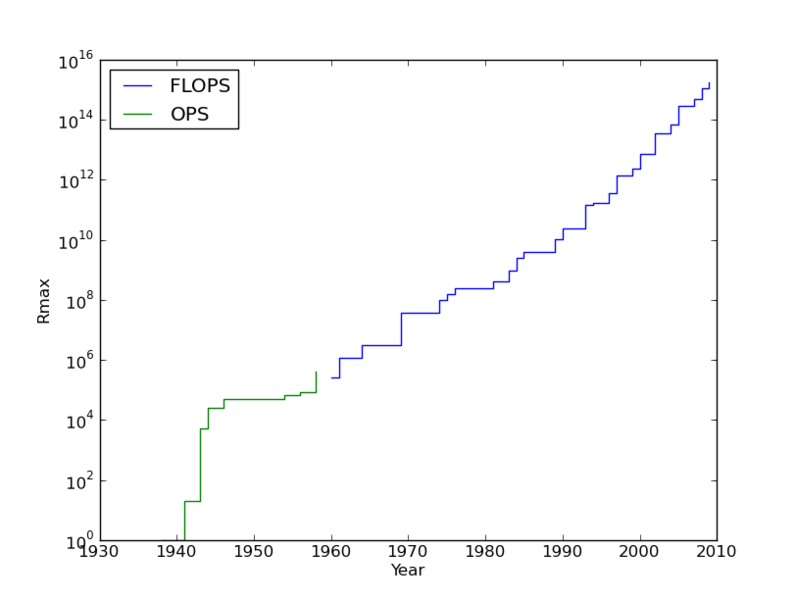
| حالي | 01:54، 21 أغسطس 2010 |  | 812 × 612 (22 كيلوبايت) | Lucaswilkins | Made it change in a stepwise manner (the graph now reflects the fact that the fastest computer changing is a discrete event) |
| 01:42، 21 أغسطس 2010 |  | 812 × 612 (28 كيلوبايت) | Lucaswilkins | {{Information |Description= First and Third columns of data taken from en.wikipedia.com/wiki/Supercomputer and put into file "sc". Removed UPenn ENIAC entry. Used python 2.6 code as follows (I make no excuses for readability/general quality): <code> #!/u |
استخدام الملف
الصفحة التالية تستخدم هذا الملف:
الاستخدام العالمي للملف
الويكيات الأخرى التالية تستخدم هذا الملف:
- الاستخدام في et.wikipedia.org