ملف:Network.jpg

حجم هذه المعاينة: 800 × 480 بكسل. البعدان الآخران: 320 × 192 بكسل | 961 × 577 بكسل.
الملف الأصلي (961 × 577 بكسل حجم الملف: 52 كيلوبايت، نوع MIME: image/jpeg)
تاريخ الملف
اضغط على زمن/تاريخ لرؤية الملف كما بدا في هذا الزمن.
| زمن/تاريخ | صورة مصغرة | الأبعاد | مستخدم | تعليق | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| حالي | 17:34، 23 نوفمبر 2010 | 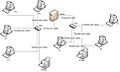 | 961 × 577 (52 كيلوبايت) | Santhan 31 | {{Information |Description={{en|1=Network Interface Cards: NICs that are on a network must have at least one protocol bound to it within the OS. This way that instance of the NIC can let the OS reach the rest of the network with that protocol. Cabling que |
استخدام الملف
الصفحة التالية تستخدم هذا الملف:
الاستخدام العالمي للملف
الويكيات الأخرى التالية تستخدم هذا الملف:
- الاستخدام في bg.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام في en.wikiversity.org
- الاستخدام في fr.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام في ha.wikipedia.org
